Cryptocurrency 101 for dummies
Understanding the need for cryptocurrency

It can be difficult to wrap your head around how cryptocurrency works. If you are tired of being clueless from hearing all the buzzwords and hype around cryptocurrency, this article is for you.
In this article, we hope to break down cryptocurrency into layman terms to help you to get a very basic understanding of it or even get started on the journey. Do note that after reading this article, it won’t make you a crypto expert but rather an extremely high-level view of it.
Disclaimer: We don’t see ourselves as crypto experts, all the information that we gathered here are based on our research and understanding.
What is Fiat Money?
Before we dive into cryptocurrency, it is important to understand a little history of our current monetary system. The most common currency that we use now is what we call “fiat money”.
Fiat money is a government-issued currency that is not backed by a commodity such as gold. It has value entirely based on trust in the government or our financial system.
Singapore is one of the richest nations in the world, being fortunate enough to be born in this city-state island it is hard to see the problem with our current financial system. But it is definitely not perfect, cryptocurrency in short aims to replace money as we know it. To understand why there is increasing adoption of cryptocurrency you need to understand the fault in our monetary system.
Problem with Fiat Money
Inefficiency
Our current financial system has come a long way, but it is still not as efficient as it can be and that is because there are multiple middlemen in between. Think about a traditional retailer business model, where a retailer has to get his goods from a distributor, the distributor will get it from a wholesaler and the wholesaler will get the goods from the manufacturer. Anywhere between the final consumer of the goods to the manufacturer is the middleman.
Removing the middleman has always resulted in better cost savings and speed. For example, it would be much cheaper if the retailer were to get the goods directly from the manufacturer.
This is the same for our financial system but this time the middleman are the banks, financial institutions, government etc. A good example to understand the inefficiency in our financial system is to take a look at how cross-border payment works.
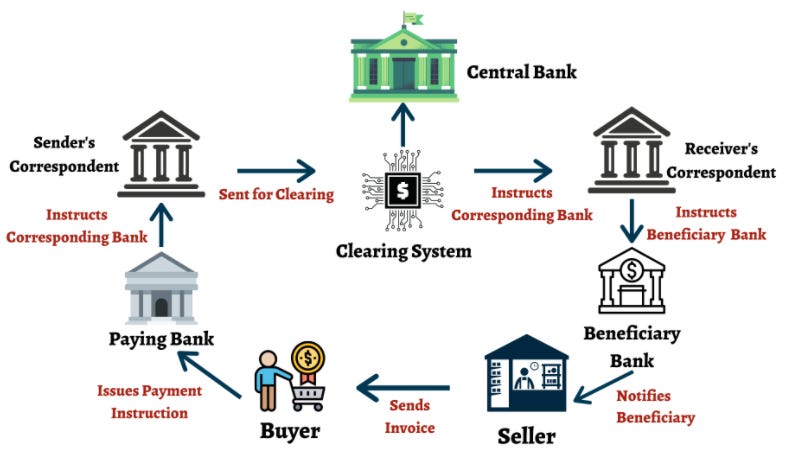
Source: The Digital Fifth
From the chart above you could see that cross-border transfer is a painstakingly long process with an expensive transactional cost. It is only until recently, talks between fast cross-payment payment transfers started to take place, you can read more about it here.
Centralisation
A centralised finance (also known as CeFi) system refers to one with a centralised platform. This platform can be managed by a person, group of people or a government body. In our local context, the Fiat money is managed by the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). The value of Fiat money is heavily influenced by the decision made by MAS. If you wish to learn more about how Singapore manages its currency you can find out more here.
It might not seem like a bad thing to have our money managed by the government. But problems may quickly arise when corruption exists within the system. The government has the power to print as much money as they wish. You can imagine how bad it can be to leave a money-printing machine in the hands of a corrupted politician.
If you have studied economics, you would have heard of hyperinflation in Zimbabwe. Long story short, an excessive supply of money would lead to the devaluation of money. The president of Zimbabwe basically printed too much of it to the point where $50 billion Zimbabwean bills are worth only $0.33 USD.
Risk of a bank run
Most money that is circulating around the economy now does not really exist. If everyone in Singapore decided to withdraw all their money from the bank, the entire financial system in Singapore will collapse and that’s the same for everywhere else in the world.
To understand this you will have to understand how banks work. When you deposit your money into a bank, they are only required to keep a percentage of it known as Require Reserve Ratio (RRR) and for the remaining balance, the bank has the freedom to loan it out to generate interest as profit.

If you look at the diagram above, the initial deposit of $1,000 actually generated a total of $2,900 in the system. Although the total amount of money circulating the system increases, there is in fact only $1,000. This is what economists call the money multiplier effect.
What this means is, if one day we lose trust in the banking system and choose to withdraw all our money, you might find out that there isn’t any to withdraw.
Accessibility
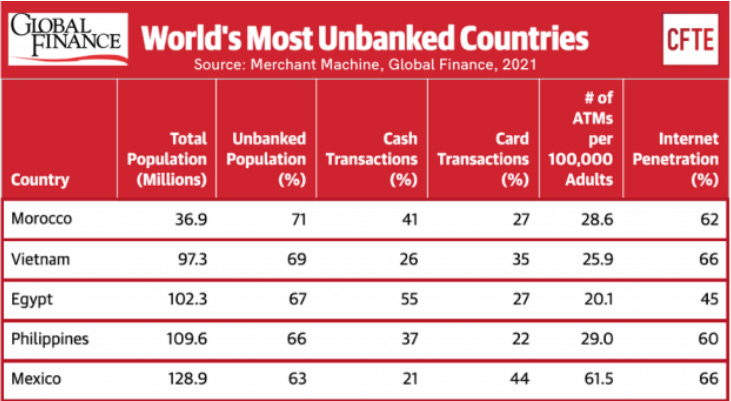
One-fourth of the global population do not have a bank account. In South-East Asia, countries like Vietnam, the Philippines and Indonesia are among the world’s most unbanked countries, with Vietnam topping the list as the world’s second. In Vietnam, 69% of its population does not have a bank account and their number of ATMs per 100,000 adults to be at 25.9 ATMs twice lower than Singapore.
This makes it extremely difficult to transfer money to these people. Imagine a scenario where you are working overseas and intend to send some money to your parents back home. However, they don’t own a bank account. What would you do? In such cases, the only way to do it is through services such as remittance which can be expensive and time-consuming.
What is cryptocurrency?
To put it simply, cryptocurrency aims to be similar to the fiat money we own now, except— it’s completely digital. Although we hardly transact with physical cash now with the high adoption of debit cards it feels like we are already at the digital cash era but every single dollar in our bank can supposedly be withdrawn via the ATM in cash. But as for cryptocurrency, there is no physical form at all.
The world that cryptocurrency promises
Decentralization
The most important concept of cryptocurrency is that it is not managed by anyone or any platform. This means that no single individual or government has the ability to control the supply of the cryptocurrency. It might be difficult to understand what it means initially but when you think about the concept of the internet, it’s pretty similar — who owns the internet?
The decentralized feature of cryptocurrency solves the potential bank run problem and hyperinflation that exist within fiat money.
Unlike fiat money, you do not have to rely on a bank or a custodian to manage it for you. You will have full control of your money, which means that it will not be “loaned” out to others unless you decide to do so.
And since no one can decide to simply “print” more money, there wouldn’t be hyperinflation as well.
Efficiency
The problem with fiat money that we raised earlier on how troublesome it is to do cross-border payment and reach out to individuals who do not have a banking system? Cryptocurrency has the potential to solve all of them by simply being on the internet.
Sending cryptocurrency theoretically can be as easy as sending an email, as long as the person has internet access he/she can receive your email. This significantly reduces the cost of transferring money and increases the speed by removing all the intermediaries. Most importantly, it gives the unbanked, access to financial services.
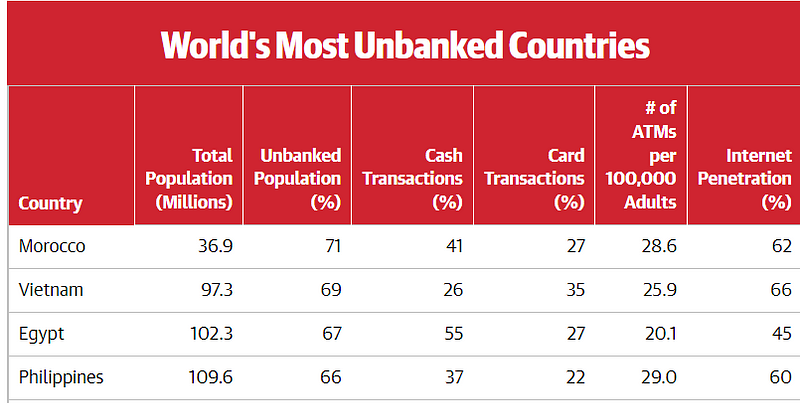
Source: Global Finance and Merchant Machine, 2021
Looking at the ranking of the world’s most unbanked countries, you can see that the internet penetration rate is much higher than the country’s banked population. This shows the potential of how cryptocurrency can positively impact the world if it were to become the new norm of what we transact.
Should you be investing in Cryptocurrency?
Well, it depends. If you are convinced that cryptocurrency would be the future of money and want to invest in it, there will be a lot of homework to be done and it will definitely be a roller coaster ride. Here are the reasons why:
First of all, you might have heard of Bitcoin and Ethereum but do you know that there are more than 6,000 cryptocurrencies out there? Nobody knows for sure which crypto currency or currencies will replace the money as we know now or well it co-exist with it. Although more established crypto like Bitcoin and Ethereum have a higher chance to reach mass adoption there is no guarantee that they will be around in decades to come.
Bitcoin is still unable to process transactions as quickly as how Visa/Mastercard works and it is actually a significant energy consumption contributor. As of 2021, Bitcoin actually consumes as much energy as the entire Netherlands. For Ethereum, it is facing a set of problems on its own. You can read more about it here to find out what it is and how the developers are trying to solve it.
Secondly, even with a perfect cryptocurrency that has no drawback, it might not make it to mass adoption as well, simply because the “marketing” is not done right. The worth of money is based on the value we give it. For fiat money, we have the words of the government that it is valuable. But for cryptocurrency, if there are very few people who see the value in it, it just wouldn’t grow.
Lastly, many central banks in the world have been experimenting with their own digital currency project. This means that in the nearby future, there is a possibility of using a fully digitalised legal dollar. Although if this project is successful, it would still be considered as a centralised system — where the government could simply create a more digital currency. Despite that, it does have the potential to solve some of the problems that fiat money presents. Such projects might affect the demand for cryptocurrency and its potential to be the future of money.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency has the potential to transform the financial system as we know it. If that were to happen and if you picked the right cryptocurrency to invest in, it is possible to get massive monetary gain out of it. But do remember that it is equally likely for you to lose all your money as well.